26-网络中的网络(NiN)
动手学深度学习李沐
26-网络中的网络(NiN)
1. 动机
全连接层的问题
- 卷积层需要的参数较少
- 而卷积层后的第一个全连接层的参数较多

以VGG为例(图示),全连接层需要先Flatten,输入维度为512x7x7,输出维度为4096,则需要参数个数为512x7x7x4096=102M。
2. NiN块
- 核心思想:一个卷积层后面跟两个1x1的卷积层,后两层起到全连接层的作用。
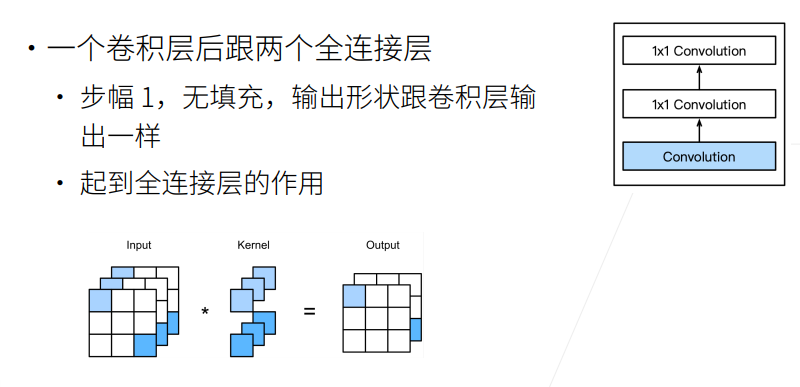
3. NiN架构
- 无全连接层
- 交替使用NiN块和步幅为2的最大池化层
- 逐步减小高宽和增大通道数
- 最后使用全局平均池化得到输出
- 其输入通道是类别数
4. NiN Networks
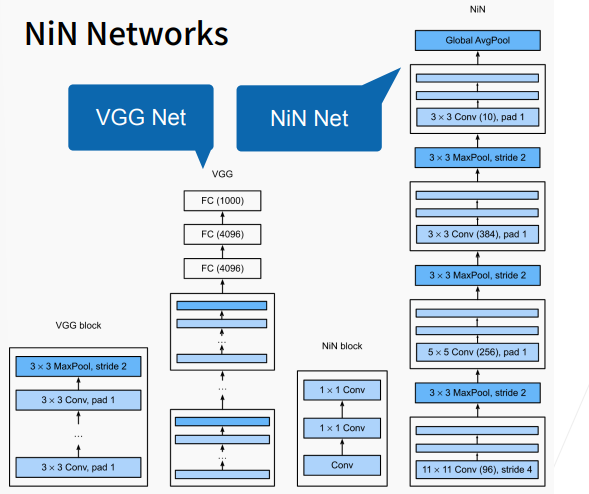
NiN架构如上图右边所示,若干个NiN块(图示中为4个块)+池化层;前3个块后接最大池化层,最后一块连接一个全局平均池化层。
5. 总结
- NiN块结构:使用卷积层加两个1x1卷积层
- 后者对每个像素增加了非线性性
- NiN使用全局平均池化层来替代VGG和AlexNet中的全连接层
- 不容易过拟合,更少的参数个数
6.代码
# 如果在Colab上跑, 或没有安装过d2l包, 需要最开始pip install d2l |
NiN块
import torch |
NiN模型
net = nn.Sequential( |
demo测试,查看每个块的输出情况
X = torch.rand(size=(1, 1, 224, 224)) |
>>> |
训练模型
lr, num_epochs, batch_size = 0.1, 10, 128 |
<Figure size 252x180 with 1 Axes> |