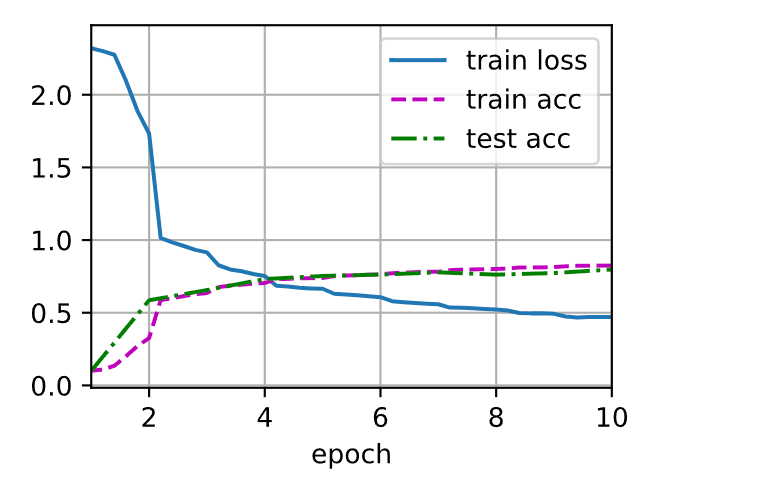
def train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, device):
"""用GPU训练模型(在第六章定义)"""
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear or type(m) == nn.Conv2d:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
net.apply(init_weights)
print('training on', device)
net.to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs],
legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc'])
timer, num_batches = d2l.Timer(), len(train_iter)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
metric = d2l.Accumulator(3)
net.train()
for i, (X, y) in enumerate(train_iter):
timer.start()
optimizer.zero_grad()
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
with torch.no_grad():
metric.add(l * X.shape[0], d2l.accuracy(y_hat, y), X.shape[0])
timer.stop()
train_l = metric[0] / metric[2]
train_acc = metric[1] / metric[2]
if (i + 1) % (num_batches // 5) == 0 or i == num_batches - 1:
animator.add(epoch + (i + 1) / num_batches,
(train_l, train_acc, None))
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, test_iter)
animator.add(epoch + 1, (None, None, test_acc))
print(f'loss {train_l:.3f}, train acc {train_acc:.3f}, '
f'test acc {test_acc:.3f}')
print(f'{metric[2] * num_epochs / timer.sum():.1f} examples/sec '
f'on {str(device)}')
|